Weekly Progress Roundup
Hopeful news on nuclear energy, the first FDA-cleared brain implant, possible alien bio-signatures, and more.
Economics & Development
Electricity access in Kenya rose from 37 percent in 2013 to 79 percent in 2023. The International Energy Agency predicts the country will reach universal electricity access by 2030.
US public support for free trade is surging, mostly on the left, as President Trump imposes new tariffs.
Energy & Environment
Conservation and biodiversity:
A new study in Endangered Species Research surveyed 48 populations of endangered sea turtles and found that a majority show signs of recovery—the latest in a growing body of research with similar conclusions.
Grey wolves are recovering in the American Southwest: “There are now at least 286 Mexican gray wolves roaming parts of New Mexico and Arizona — 11 percent more than the previous year, marking the ninth straight year that the population of endangered animals has grown.”
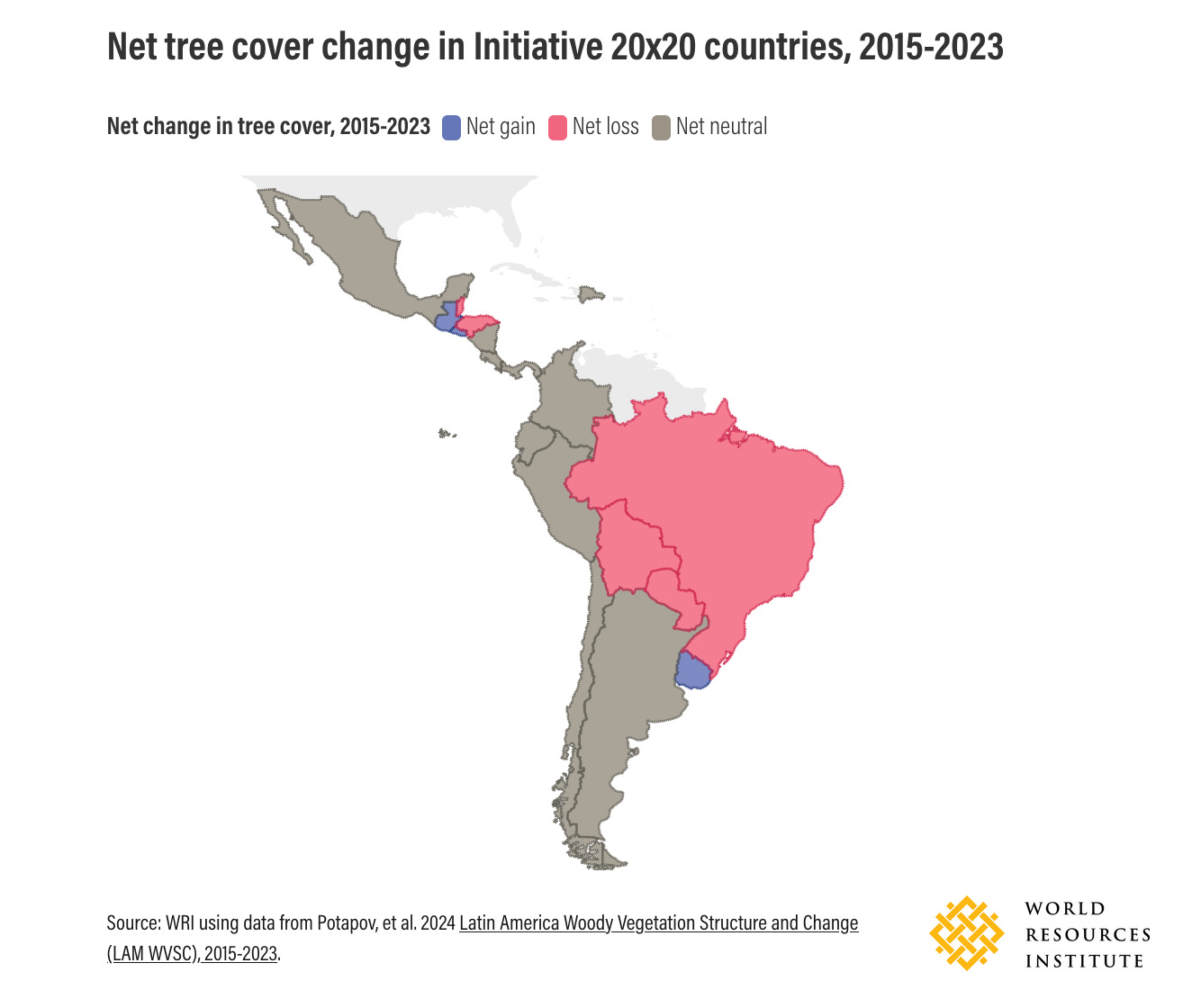
While Latin America is losing forest area overall, deforestation is under control in much of the region. Out of the 18 countries included in a recent University of Maryland study of satellite data, 13 showed stable or growing tree cover between 2015 and 2023.
Energy production:
A recent Gallup poll found 61 percent of Americans now support nuclear energy. The last time public support for nuclear was this high was 2010, just before the much-sensationalized Fukushima disaster.
The World Bank may soon end its ban on funding nuclear energy projects. Reuters reports that World Bank President Ajay Banga is pursuing an “all of the above” energy strategy that includes “natural gas, geothermal, hydroelectric, solar, wind and nuclear power.”
For the first time in the United States, a commercial nuclear reactor has begun testing fuel enriched up to 6 percent uranium-235, exceeding the industry standard of 3 to 5 percent. More concentrated fuel allows reactors to operate longer before refueling, generate more power, and produce less waste.
Two US firms, Dow Chemical and X-energy, have jointly applied to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to build small modular nuclear reactors at a Texas chemical plant. If all goes to plan, this could be the first US factory powered by onsite nuclear energy.
Pollution:
New research from Australia’s national science agency suggests coastal plastic pollution Down Under fell 39 percent between 2013 and 2023.
Researchers in China have found that the water hyacinth—a prolific South American species that has colonized waterways around the world—is highly effective at absorbing microplastics. Within 48 hours, the hyacinths had removed more than half of the plastic particles in highly contaminated water. Remarkably, the plants were still healthy two weeks after the exposure.
Health & Demographics
Eli Lilly has announced the results of a clinical trial of a GLP-1 agonist weight loss pill. The drug, called orforglipron, functions similarly to semaglutide (Ozempic) but does not need to be injected or refrigerated. And, thanks to its molecular structure, orforglipron should also be much cheaper and easier to produce.
After over a decade of research, a wave of stem cell treatments are now showing promising results in trials, including for vision loss, Parkinson’s disease, and spinal cord injuries.
Surgeons in Taiwan have pioneered a new method of heart transplantation. Instead of keeping the donor heart on ice, they used a special machine that continuously pumped oxygenated blood through the organ, reducing both damage to the heart and the risk of rejection.
Nitisinone, a drug typically used to treat metabolic disorders, was recently shown to be incredibly deadly to mosquitos. Writing in Quillette, physician and biologist Henry Miller notes that the blood of a person taking even low doses of the drug can kill mosquitos within 24 hours, offering a potential new method of mosquito control.
South America is making progress toward eliminating foot-and-mouth disease, a highly contagious virus that primarily affects animals like cows, pigs, sheep, and goats. According to the Pan American Health Organization, over 65 percent of cattle in South America now live in areas that are recognized as free of the disease. While foot-and-mouth disease is not a serious threat to humans, it can have a devastating impact on animal agriculture.
Science & Technology
Astronomers using NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have detected possible signs of extraterrestrial life. The evidence consists of the spectral signatures of two gases, dimethyl sulfide (DMS) and dimethyl disulfide (DMDS), on a world with a habitable orbit and possibly a planet-wide ocean. The latter is an especially important part of the story: On Earth, these gases are produced only by living creatures, and primarily by marine phytoplankton. However, this isn’t a smoking gun—DMS and DMDS can be produced abiotically, and the signatures could turn out to be instrumental artifacts.
Precision Neuroscience has become the first company to receive FDA clearance for a wireless brain implant, allowing them to market and sell their device to medical practitioners for uses such as mapping brain activity during surgeries. In trials, similar implants have enabled paralyzed people to operate computers with their minds and translated thoughts into speech in near-real time.