Doomslayer: Weekly Progress Roundup
Divorce rates are down, clean fuel access is up, and a fusion company claims it knows how to turn mercury into gold.
Announcements
Our managing editor Chelsea Follett’s book, Centers of Progress, was recently republished in Korean. This new edition features a beautifully redesigned cover and many more photos and illustrations than the original.
Culture & Tolerance
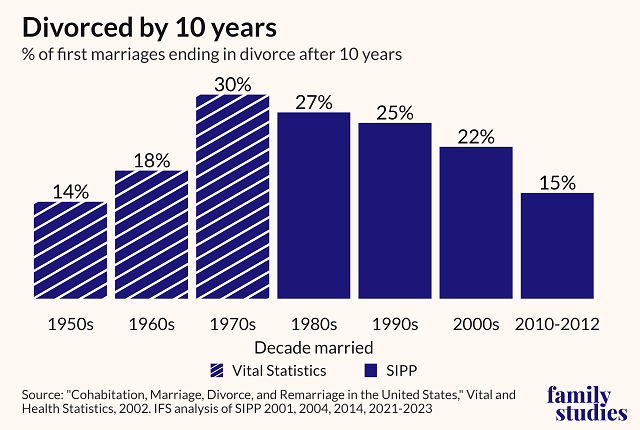
According to recent research from the Institute for Family Studies, US marriages in the early 2010s were more stable than marriages during any other decade since the 1950s. They estimate that 15 percent of couples that first married between 2010 and 2012 were divorced after 10 years, down from a high of 30 percent in the 1970s.
Energy & Environment
Conservation and biodiversity
The Baltic ringed seal population grew from around 5,000 in 1970 to an estimated 25,000 in 2024, thanks to hunting bans and a decline in environmental toxins.
In Kazakhstan, the population of saiga antelopes has surged from fewer than 30,000 in 2003 to over 4 million today. Now, the Kazakh government is sending 1,500 saigas to China to accelerate the recolonization of the antelope’s historic range.
Reintroducing wolves to Yellowstone has triggered a resurgence of aspen trees. A new study found that one-third of aspen groves in the park now have healthy young trees—something not observed since the 1940s—thanks to the reduced elk population.
Energy & Natural Resources
A new oil discovery may more than double Poland’s known oil reserves.
The nuclear fusion startup Marathon Fusion published a paper claiming that fusion reactors could one day transmute mercury into gold, potentially creating 5,000kg of the precious metal per gigawatt-year without sacrificing energy output.
A startup in New Zealand has developed a chemical process that can produce valuable materials from olivine, a cheap, common mineral. Using just olivine, sulfuric acid, water, and electricity, the method generates silica, magnesium hydroxide, and, most importantly, nickel-manganese-cobalt hydroxide, an important material in lithium-ion batteries.
Health & Demographics
Since 2010, nearly 1.5 billion people in Asia and Latin America have gained access to clean cooking stoves and fuels, helping reduce deadly indoor air pollution and environmental harm.
Scientists have developed a genetic tweak in mosquitoes that blocks the spread of malaria. By changing just one part of a mosquito protein, they made it so the insects can still carry the parasite but can’t pass it on when they bite. The change spreads naturally through mosquito populations and doesn’t harm their health, making it a promising tool for stopping malaria in the wild.
A non-hormonal birth control pill for men has passed its first human safety trial.
Science & Technology
AI models from Google and OpenAI achieved gold medal-worthy scores in the International Mathematical Olympiad, a math competition for high school students.
Google DeepMind has developed an AI tool called Aeneas that can help historians decode and restore ancient Roman inscriptions. Trained on data from nearly 200,000 Latin texts, Aeneas can suggest missing words, date inscriptions within 13 years, and identify the province of origin with a fair level of accuracy.
Progress Studies
Daniel Jeffries imagines life in a future of “ambient AI.”
Derek Thompson reviews the research on GLP-1 drugs and their wide-ranging effects.
Matt Yglesias clears the air on AI water use.






Ask greats great friend 🧡
Did you do a story on the recovery of the Great Barrier Reef? It would be interesting to see a well researched update on the situation there.