Doomslayer: Progress Roundup
Critical minerals in Utah, an impressive weight-loss drug, fake catastrophes, and more.
Economics & Development
Argentina’s poverty rate has fallen to 36 percent in the third quarter of 2025, roughly 9 percentage points lower than the same period last year, amid slowing inflation.
Energy & Environment
Ionic Mineral Technologies has discovered high concentrations of 16 critical minerals—including lithium, germanium, and cesium—in a clay deposit in Utah. The full extent of the find is unknown, but the company claims it could be “the most significant critical mineral reserve in the US.”
The endangered Palau ground dove is showing signs of recovery on Ulong Island in the Pacific following a successful rat eradication.
A recently published analysis of the ecological impacts of deep-sea mining found that, unsurprisingly, scraping off the first few centimeters of the seafloor sharply reduced animal life along the machine’s path. However, researchers found no evidence that sediment kicked up by the mining vehicle reduced overall animal abundance in the wider area—something many scientists had feared.
Health & Demographics
In a late-stage trial, Eli Lilly’s experimental obesity drug retatrutide delivered some of the best weight-loss results ever seen. Patients on the highest dose lost nearly 29 percent of their body weight over 68 weeks. Across all treated participants, average weight loss was about 24 percent, appearing to outperform currently approved drugs like semaglutide and tirzepatide.
The FDA has approved two new oral antibiotics to treat gonorrhea, the first new oral therapies for uncomplicated gonorrhea in decades. These new drugs are especially important because the bacteria that cause gonorrhea have been evolving resistance to most existing treatments.
A new study strengthens the case that the shingles vaccine might lower dementia risk. By using an age-based rollout in Wales as a natural experiment, scientists found vaccinated elderly people were about 20 percent less likely to develop dementia over seven years than those just outside the eligibility cutoff.
This study examined Zostavax, a discontinued shingles vaccine, not the currently used Shingrix vaccine.
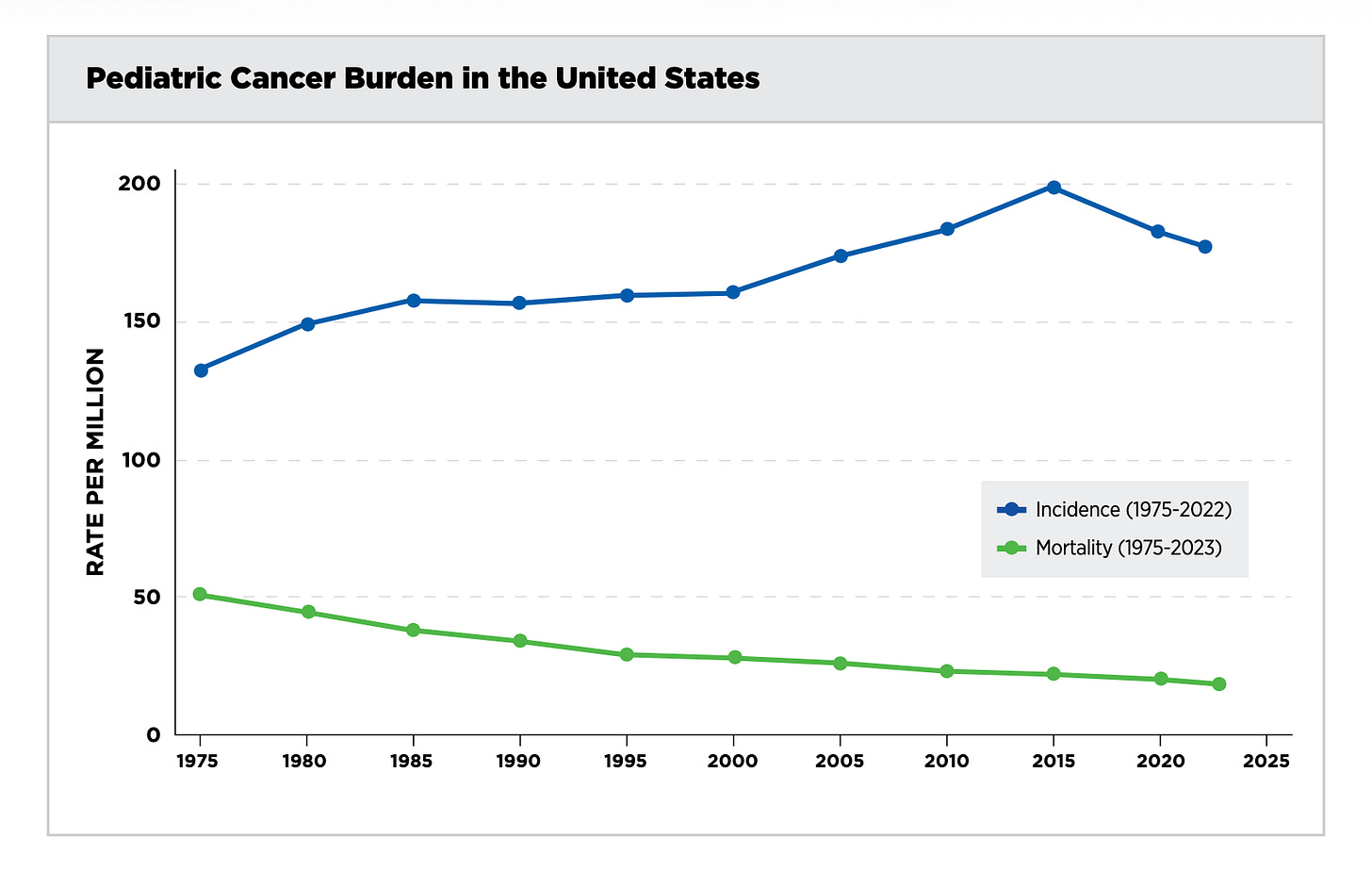
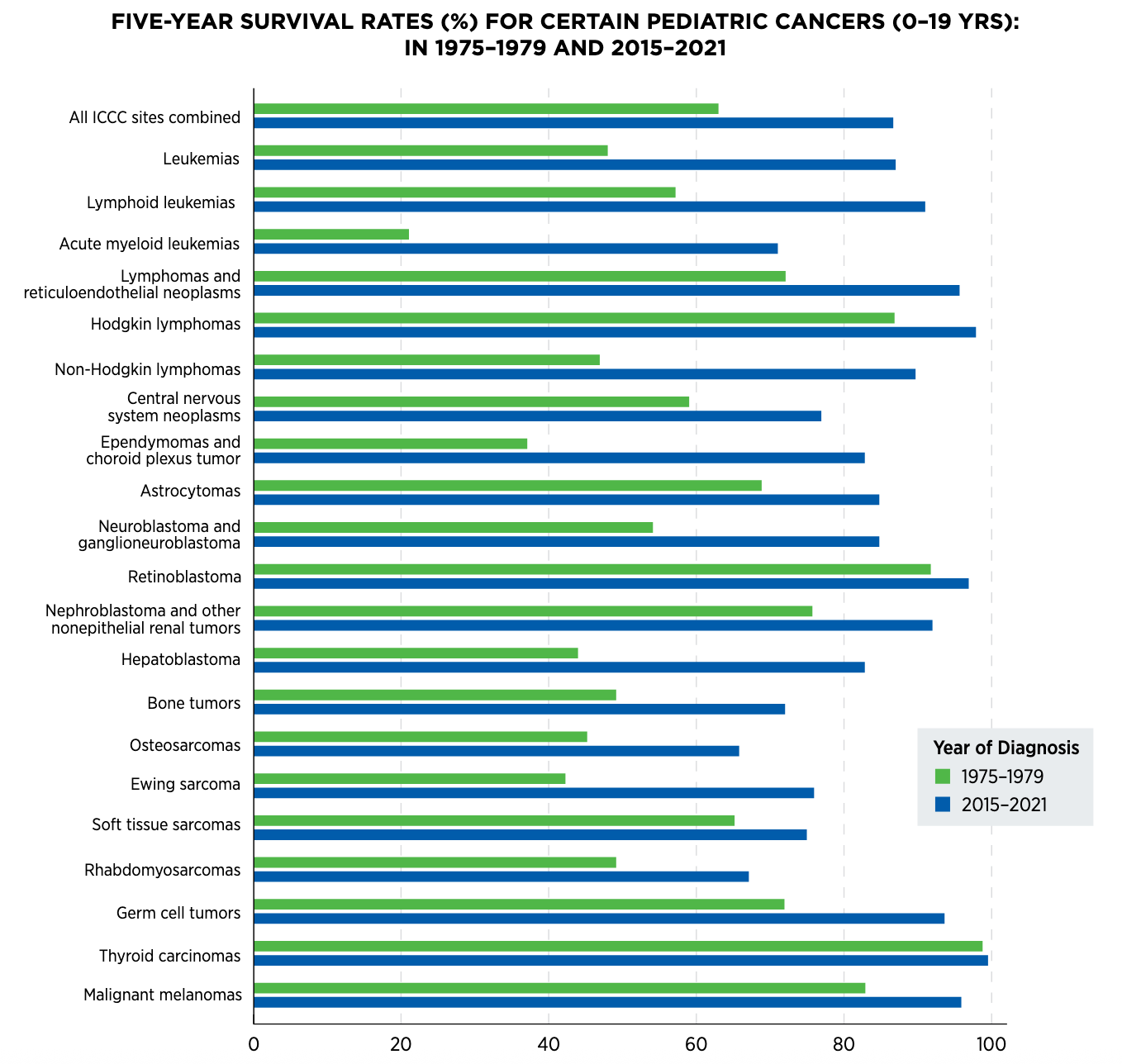
The American Association for Cancer Research has a new report highlighting some incredible progress against pediatric cancer in the United States, including a roughly two-thirds decline in the death rate since the 1970s.
According to CDC data compiled by Jeff Asher, deaths in the United States caused by homicides, traffic accidents, drug overdoses, and alcohol are all down significantly from their early-2020s peaks.
*Note that the 2025 data on this chart only include January.
Science & Technology
Aurora Innovation, a self-driving truck company, is expanding its operations in Texas. In 2026, it plans to launch a fleet of autonomous trucks to haul sand used for oil and gas drilling around the Permian Basin.
A startup called Overview Energy has completed a major engineering milestone for space-based solar power, successfully beaming energy from a moving aircraft to a ground receiver. The company plans to use the same method and similar hardware to transmit power from satellites in orbit.
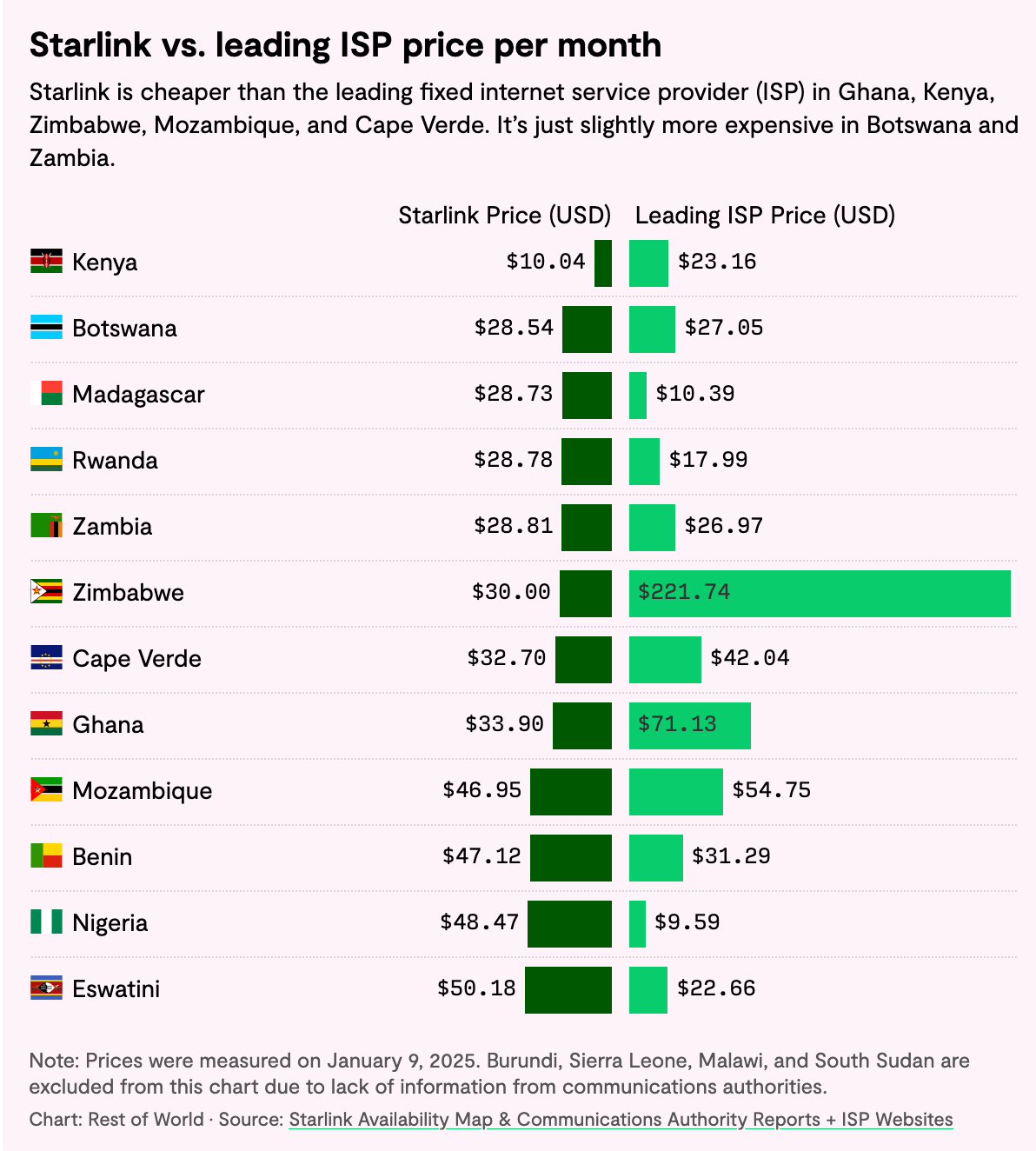
In many developing countries, Starlink provides much faster and more reliable internet connection than local providers. In at least five African countries—Ghana, Kenya, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, and Cape Verde—it is also cheaper than the leading provider.
Andy Masley, a blogger and effective altruist who has done great work correcting misconceptions about AI resource use, has compiled a list of other “fake catastrophes,” from falling testosterone to low teacher pay. I recommend checking it out to see if you’ve fallen for any of these:



"The shingles vaccine" is ambiguous. The cited study used a live-attenuated herpes zoster vaccine. It says, "our results pertain to the live-attenuated HZ vaccine (Zostavax, Merck) only, because the newer recombinant HZ vaccine (Shingrix, GSK) was introduced into the UK’s National Health Service after our follow-up period ended." Zostavax was discontinued in the U.S. in 1920.