Doomslayer: Progress Roundup
Tortoise de-extinction, solar and nuclear energy records, cleaner waters, and more.
To better respect your inbox and your time, progress roundups will be sent biweekly going forward. You’ll receive the same amount of content, just delivered less frequently.
Energy & Environment
Conservation and biodiversity
A 2024 census found 5,326 jaguars in Mexico, 30 percent more than the 2010 count.
In other jaguar news, a cub has been spotted in northwestern Argentina—the first known wild jaguar birth in the region since the 1990s.
The non-profit Rewilding Spain is introducing Przewalski’s horses and aurochs-lookalike Taurus cattle to the Spanish countryside in an attempt to fill the ecological niches left empty by the long-extinct European megafauna.
In the 19th century, hungry whalers hunted the Floreana giant tortoise to extinction. But because the tortoises were often kept alive aboard ships, some ended up as castaways on neighboring Galápagos islands, where they interbred with local giant tortoise subspecies. In 2000, scientists identified these hybrids and, in the 2010s, began selectively breeding them back toward the original Floreana lineage. Hundreds of juveniles have since hatched, and now the “resurrected” subspecies is being reintroduced to its home island.
Energy & Natural Resources
Global solar additions reached nearly 600 gigawatts in 2024, and the pace has quickened—380 gigawatts were installed in the first half of 2025, putting this year on track for another record.
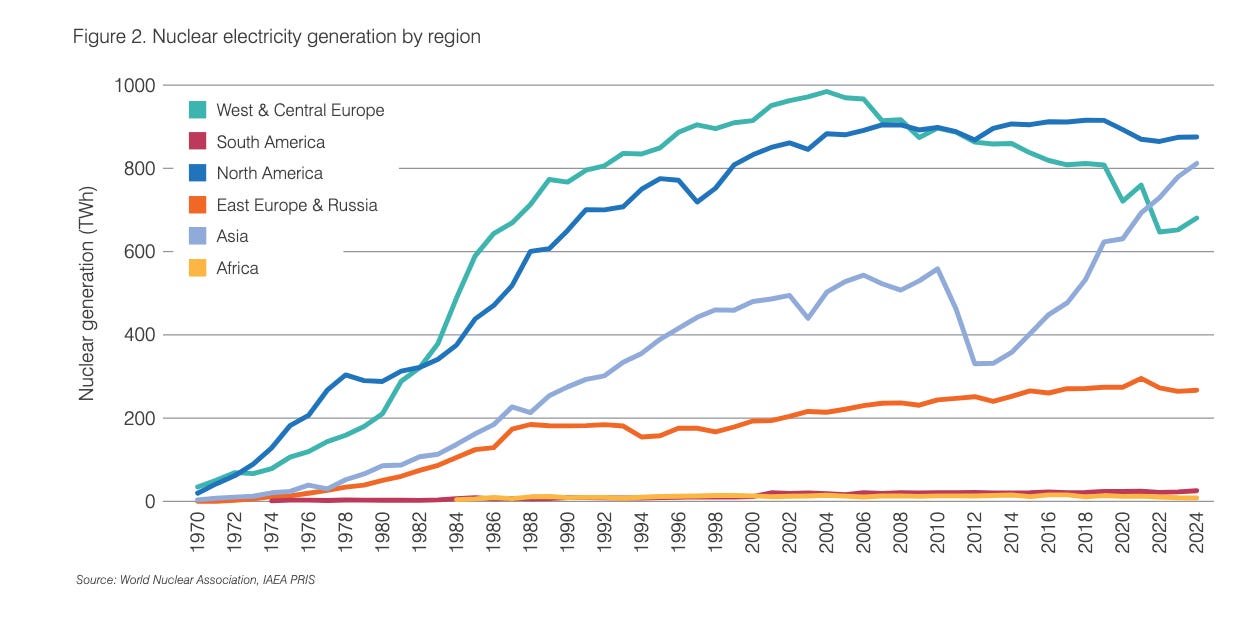
The latest World Nuclear Performance Report claims that nuclear energy generation reached a record 2667 terawatt-hours in 2024, narrowly surpassing the previous record of 2660 terawatt-hours in 2016.
Over the past decade, almost all the growth in nuclear energy generation occurred in Asia—home to 59 of the 70 nuclear reactors currently under construction—while generation in Western Europe fell substantially.
Fortunately, a policy shift is now underway that might end this ill-advised nuclear phase-out.
Pollution
Thanks to improved infrastructure and pollution control, the number of fish species living in the Chicago River has surged from 5 in the 1970s to more than 70 today. Humans are another species newly utilizing the river: in two weeks, the city plans to host its first Chicago River swim since 1927.
China is also reporting significant progress against water pollution. According to the Chinese Ministry of Ecology and Environment, the share of surface waters “suitable for drinking, fishing and direct human contact” grew from 63 percent to 90.4 percent between 2014 and 2024.
Health & Demographics
Togo has added the malaria vaccine to its national immunization program.
Child nutrition is improving in rapidly-developing Vietnam. Between 2010 and 2024, the share of children who were underweight fell from 17.5 percent to 10.4 percent. The country has made similar progress against childhood stunting, anemia, and vitamin deficiency.
Science & Technology
Waymo has announced plans to bring its robotaxi service to Denver and Seattle.
Monumental Labs, a startup based in Brooklyn, is trying to automate stone carving. The company uses robotic arms to sculpt statues and facades, and has already helped restore parts of Carnegie Hall and the Frick Museum. For now, Monumental can carve pieces up to 12 feet tall, but they have ambitions to scale up their process until it can tackle giant structural stone blocks.



Lots of good news -- apart from the increased deployment of solar which is raising costs, decreasing reliability, and destabilizing the grid.